DataLoader + pin_memory
Disclaimer: This post has been translated to English using a machine translation model. Please, let me know if you find any mistakes.
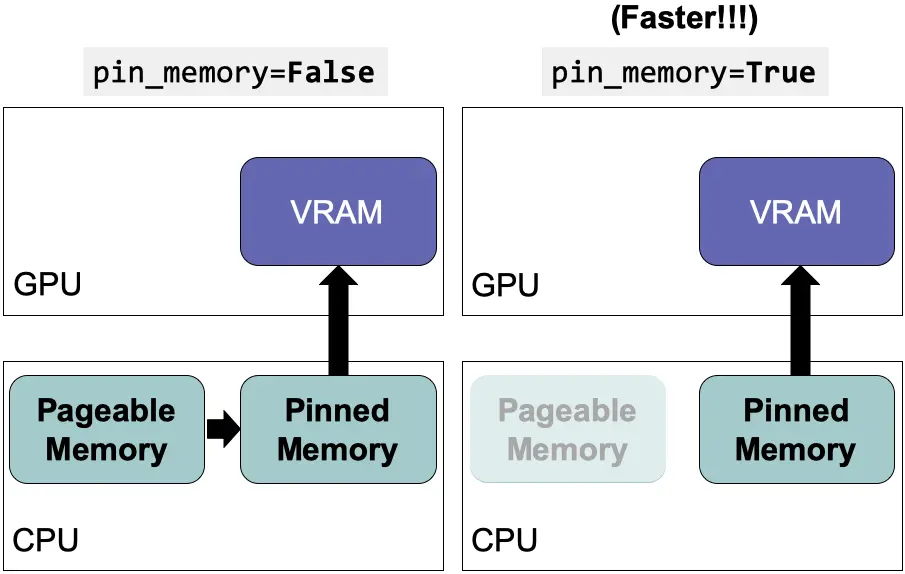
In PyTorch, when training neural networks, especially on large datasets, leveraging the DataLoader with pin_memory=True and setting num_workers to a positive number significantly increases performance.
pin_memory=True allows for faster transfer of data to the GPU by keeping it in pinned (page-locked) memory.
At the same time, num_workers determines the number of subprocesses used for data loading, allowing for asynchronous data retrieval without blocking the GPU calculation
This combination minimizes the GPU downtime, ensuring more efficient use of hardware resources and faster model training times.
data_loader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=32, shuffle=True, num_workers=4, pin_memory=True)